N,N-ジメチルエチルアミン
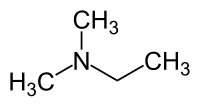
N,N-ジメチルエチルアミン(英語: N,N-Dimethylethylamine、DMEA)は、化学式が (CH3)2NC2H5 の有機化合物である。主に鋳物工場でエポキシ樹脂やポリウレタンの触媒として、また中子砂の製造に使用される工業用化学物質である[2][3]。ジメチルエチルアミンは、室温で悪臭を放つ揮発性の液体で、トリメチルアミンの食事からの摂取量が多いほど、高濃度で排泄される[1] 。
| N,N-ジメチルエチルアミン | |
|---|---|
| |
N,N-Dimethylethanamine | |
別称 Ethyl(dimethyl)amine | |
| 識別情報 | |
| CAS登録番号 | 598-56-1 |
| PubChem | 11723 |
| ChemSpider | 11230 |
| UNII | 9N5384XVEM |
| 5523 | |
| |
| 特性 | |
| 化学式 | C4H11N |
| モル質量 | 73.14 g mol−1 |
| 外観 | 室温で揮発性の液体 |
| 密度 | 0.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
| 融点 |
-140 °C, 133 K, -220 °F |
| 沸点 |
36.5 °C, 310 K, 98 °F |
| 蒸気圧 | 495.4±0.1 mmHg |
| 酸解離定数 pKa | 10.16 (共役酸) (H2O)[1] |
| 特記なき場合、データは常温 (25 °C)・常圧 (100 kPa) におけるものである。 | |
出典
編集- ^ a b “N,N-Dimethylethylamine”. Toxnet. Hazardous Substance Data Bank. 16 September 2018時点のオリジナルよりアーカイブ。4 May 2014閲覧。 “The aim was to study the effect of trimethylamine (TMA) on the metabolism of the industrial catalyst N,N-dimethylethylamine to ascertain whether biological monitoring of industrial exposure to N,N-dimethylethylamine is compromised and excretion of the malodorous N,N-dimethylethylamine in sweat and urine is increased by dietary intake of TMA....Although the increased urinary and hidrotic excretion of N,N-dimethylethylamine may contribute to body odor problems, they were primarily due to TMA excretion, which is much the greater.”
- ^ Eller, Karsten; Henkes, Erhard; Rossbacher, Roland; Höke, Hartmut (2005), "Amines, Aliphatic", Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_001。
- ^ “Dimethylethylamine”. BASF The Chemical Company. 4 May 2014閲覧。