ジクロロヨードメタン
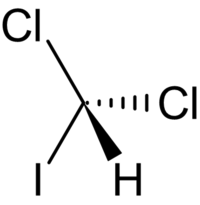
ジクロロヨードメタン(Dichloroiodomethane, DCIM)は、化学式CHCl2Iのトリハロメタンである。クロロホルム様の匂いを持つ、重く、不燃性で、透明で淡黄色の液体である[1]。アセトン、ジエチルエーテル、エタノール、ベンゼン等の有機溶媒に可溶である[2]。空気や光に接すると分解する。消毒処理された水道水から検出されており、汚染物質と見なされている[3]。水中での半減期は、275年と推定されている[4]。
| ジクロロヨードメタン | |
|---|---|
| |
dichloro(iodo)methane | |
別称 DCIM, Chloriodoform (archaic),[1] IDCM, iododichloromethane | |
| 識別情報 | |
| CAS登録番号 | 594-04-7 |
| PubChem | 11655 |
| ChemSpider | 11165 |
| UNII | 59FJY8K9MX |
| |
| |
| 特性 | |
| 化学式 | CHCl2I |
| モル質量 | 210.83 g mol−1 |
| 外観 | 淡黄色液体 |
| 沸点 |
131℃[2] |
| 水への溶解度 | 非常にわずか |
| 特記なき場合、データは常温 (25 °C)・常圧 (100 kPa) におけるものである。 | |
ヨードホルム発見の2年後の1824年にw:Georges-Simon Serullasが発見した[1]。
合成
編集多くの合成経路が知られている。クロロホルムとヨウ化ナトリウム[5]またはヨードエタン[6]の反応でジクロロヨードメタンが生じる。より古い方法には、五塩化リンまたは塩化水銀(II)とともにヨードホルムを蒸留する方法もある[1]。
出典
編集- ^ a b c d Leopold Gmelin, Henry Watts, Chloriodoform in Hand-book of Chemistry (1848), pages 337–339
- ^ a b D213 Dichloroiodomethane, The Dictionary of substances and their effects, p. 324
- ^ Emma Goslan, Kenneth Clive Thompson, Simon Gillespie, Disinfection By-products in Drinking Water (2015), Royal Society of Chemistry
- ^ Liu, David H. F; Liptak, Bela G, Groundwater and surface water pollution, page 57
- ^ Determination of Dichloroiodomethane in Water (1996)
- ^ Nariyoshi Kawabata, Masami Tanimoto, Shigehiro Fujiwara. Synthesis of monohalocyclopropane derivatives from olefins by the reaction with trihalomethanes and copper, Tetrahedron, 1979