シクロ(18)炭素
シクロ[18]炭素(cyclo[18]carbon)またはシクロオクタデカ-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-ノナイン(Cyclooctadeca-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-nonayne)は、分子式C18の炭素の同素体である。18個の炭素原子が三重結合と単結合で交互に結合した環であり、ポリイン、シクロ炭素である。
| Cyclo[18]carbon | |
|---|---|
Cyclooctadeca-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-nonayne | |
| 識別情報 | |
| CAS登録番号 | 126487-09-0 |
| PubChem | 14940714 |
| ChemSpider | 74015635 |
| |
| |
| 特性 | |
| 化学式 | C18 |
| モル質量 | 216.19 g mol−1 |
| 特記なき場合、データは常温 (25 °C)・常圧 (100 kPa) におけるものである。 | |
シクロ[18]炭素は、熱力学的安定性を持つと予測される最小のシクロ[n]炭素であり、計算されるひずみエネルギーは、1モル当たり72 kcalである[1][2]。122 K以上の温度では分解してグラファイトとなる[2]。
IBMとオックスフォード大学の共同研究チームにより、シクロブタノン構造のいくつかの部位を電気化学的方法による脱カルボニル化することで[3]、2019年に固体状態での合成が主張された[4]。後にスペインの研究者がコンピュータにより分子の構造的及び電気的性質を調べ、この分子が電子受容体であることを発見した[5]。
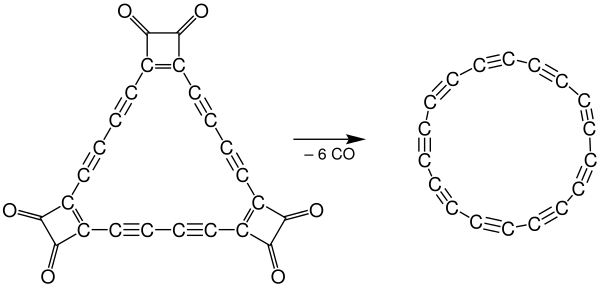
IBMの研究者によると、彼らの生成物の電子構造は、二重結合が連続したクムレン型ではなく、交互に並ぶ三重結合と単結合から構成されていた。これにより、恐らくこの分子は半導体であると考えられている[3]。
出典
編集- ^ George A. Adamson; Charles W. Rees (1996). “Towards the total synthesis of cyclo[n]carbons and the generation of cyclo[6]carbon”. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1 (13): 1535?1543. doi:10.1039/P19960001535.
- ^ a b Francois Diederich; Yves Rubin; Carolyn B. Knobler; Robert L. Whetten; Kenneth E. Schriver; Kendall N. Houk; Yi Li (8 September 1989). “All-Carbon Molecules: Evidence for the Generation of Cyclo[18]carbon from a Stable Organic Precursor”. Science 245 (4922): 1088?1090. Bibcode: 1989Sci...245.1088D. doi:10.1126/science.245.4922.1088. PMID 17838807.
- ^ a b Castelvecchi, Davide (15 August 2019). “Chemists make first-ever ring of pure carbon” (英語). Nature 572 (7770): 426. doi:10.1038/d41586-019-02473-z. PMID 31431741.
- ^ Kaiser, Katharina; Scriven, Lorel M.; Schulz, Fabian; Gawel, Przemyslaw; Gross, Leo; Anderson, Harry L. (15 Aug 2019). “An sp-hybridized molecular carbon allotrope, cyclo[18]carbon”. Science 365 (6459): 1299?1301. arXiv:1908.05904. doi:10.1126/science.aay1914.
- ^ Stasyuk, Anton J.; Stasyuk, Olga A.; Sola, Miquel; Voityuk, Alexander A. (29 Nov 2019). “Cyclo[18]carbon: the smallest all-carbon electron acceptor”. Chemical Communications 56: 352?355. doi:10.1039/c9cc08399e. hdl:10256/17613.