キスカル酸
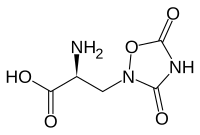
キスカル酸(キスカルさん、quisqualic acid)は、AMPA型グルタミン酸受容体及び代謝型グルタミン酸受容体のアゴニストである[1][2][3]。興奮毒性を示し、神経科学では脳や脊髄の神経細胞を選択的に破壊するために用いられる[4][5][6]。東北大学の竹本常松らにより駆虫薬として用いられる熱帯アジア原産のシクンシ(Combretum indicum)の種子から発見され、シクンシの当時の学名(Quisqualis indica)にちなみ命名された[7]。
| キスカル酸 | |
|---|---|
| |

|

|
(2S)-2-amino-3-(3,5-dioxo-1,2,4- | |
| 識別情報 | |
| CAS登録番号 | 52809-07-1 |
| PubChem | 40539 |
| ChemSpider | 37038 |
| KEGG | C08296 |
| MeSH | Quisqualic+Acid |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL279956 |
| 1372 | |
| |
| |
| 特性 | |
| 化学式 | C5H7N3O5 |
| モル質量 | 189.126 g/mol |
| 外観 | 無色結晶 |
| 融点 |
187-188℃(分解) |
| 特記なき場合、データは常温 (25 °C)・常圧 (100 kPa) におけるものである。 | |
アメリカ合衆国農務省の農業研究局による研究では、ゼラニウムの花弁にも存在することが示され、またマメコガネの麻痺の原因になっていることが明らかとなった[8][9]。キスカル酸は、昆虫の神経筋接合部やほ乳類の中枢神経系で神経伝達物質として働くL-グルタミン酸を模倣していると考えられている[10]。
出典
編集- ^ Jin R, Horning M, Mayer ML, Gouaux E. Mechanism of activation and selectivity in a ligand-gated ion channel: structural and functional studies of GluR2 and quisqualate. Biochemistry. 2002 Dec 31;41(52):15635-43. PMID 12501192
- ^ Kuang D, Hampson DR. Ion dependence of ligand binding to metabotropic glutamate receptors. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2006 Jun 23;345(1):1-6. PMID 16674916
- ^ Zhang W, Robert A, Vogensen SB, Howe JR. The relationship between agonist potency and AMPA receptor kinetics. Biophysical Journal. 2006 Aug 15;91(4):1336-46. PMID 16731549
- ^ Muir JL, Page KJ, Sirinathsinghji DJ, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ. Excitotoxic lesions of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons: effects on learning, memory and attention. Behavioural Brain Research. 1993 Nov 30;57(2):123-31. PMID 7509608
- ^ Giovannelli L, Casamenti F, Pepeu G. C-fos expression in the rat nucleus basalis upon excitotoxic lesion with quisqualic acid: a study in adult and aged animals. Journal of Neural Transmission. 1998;105(8-9):935-48. PMID 9869327
- ^ Lee JW, Furmanski O, Castellanos DA, Daniels LA, Hama AT, Sagen J. Prolonged nociceptive responses to hind paw formalin injection in rats with a spinal cord injury. Neuroscience Letters. 2008 Jul 11;439(2):212-5. PMID 18524486
- ^ 竹本常松、高木信也、中島正、在原重信、小池一弘、「使君子の成分キスカル酸の構造」、天然有機化合物討論会講演要旨集 (16), 256-263, 1972年10月1日
- ^ Geraniums and Begonias: New Research on Old Garden Favorites (the March 2010 issue of Agricultural Research magazine.)
- ^ Ranger, C.M., Winter, R. E., Singh, A. P., Reding, M. E., Frantz, J. M., Locke, J. C., and Krause, C. R. 2011. Rare excitatory amino acid from flowers of zonal geranium responsible for paralyzing the Japanese beetle. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. http://www.pnas.org/content/early/2010/12/29/1013497108.full.pdf+html
- ^ Usherwood, P. N. R. 1994. Insect glutamate receptors. Advances in Insect Biochemistry and Physiology. 24: 309-341.
]