3-メトキシチラミン
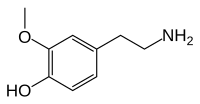
3-メトキシチラミン(3-Methoxytyramine, 3-MT)または3-メトキシ-4-ヒドロキシフェネチルアミン(3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenethylamine)は、神経伝達物質であるドーパミンの代謝物質として生じるアミンである[1]。カテコール-O-メチルトランスフェラーゼ(COMT)によって、ドーパミンにメチル基を導入することで形成される。3-MTはさらにモノアミンオキシダーゼ(MAO)によってホモバニリン酸(HVA)へ代謝され、これが尿中に排出される。
| 3-メトキシチラミン | |
|---|---|
| |

| |
4-(2-aminoethyl)-2-methoxyphenol | |
別称 3-O-methyldopamine | |
| 識別情報 | |
| CAS登録番号 | 554-52-9 |
| PubChem | 1669 |
| ChemSpider | 1606 |
| MeSH | 3-methoxytyramine |
| 6642 | |
| |
| |
| 特性 | |
| 化学式 | C9H13NO2 |
| モル質量 | 167.21 g/mol |
| 特記なき場合、データは常温 (25 °C)・常圧 (100 kPa) におけるものである。 | |
生成
編集天然には、オプンティアに含まれ[3]、サボテン科は広く持っている[4]。また、タバコ属のクラウンゴールでも見られる[5]。
関連項目
編集出典
編集- ^ a b c Khan MZ, Nawaz W (October 2016). "The emerging roles of human trace amines and human trace amine-associated receptors (hTAARs) in central nervous system". Biomed. Pharmacother. 83: 439–449. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2016.07.002. PMID 27424325。
- ^ Sotnikova TD, Beaulieu JM, Espinoza S, et al. (2010). "The dopamine metabolite 3-methoxytyramine is a neuromodulator". PLOS ONE. 5 (10): e13452. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0013452. PMC 2956650. PMID 20976142。
- ^ Neuwinger, Hans Dieter (1996). “Cactaceae”. African ethnobotany: poisons and drugs: chemistry, pharmacology, toxicology. CRC Press. pp. 271. ISBN 978-3-8261-0077-2 Retrieved on June 12, 2009 through Google Book Search.
- ^ Smith T. A. (1977). “Phenethylamine and related compounds in plants”. Phytochemistry 16: 9-18. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(77)83004-5.
- ^ Mitchell S. D.; Firmin J. L.; Gray D. O. (1984). “Enhanced 3-methoxytyramine levels in crown gall tumours and other undifferentiated plant tissues”. Biochem. J. 221: 891-5. doi:10.1042/bj2210891. PMC 1144120.